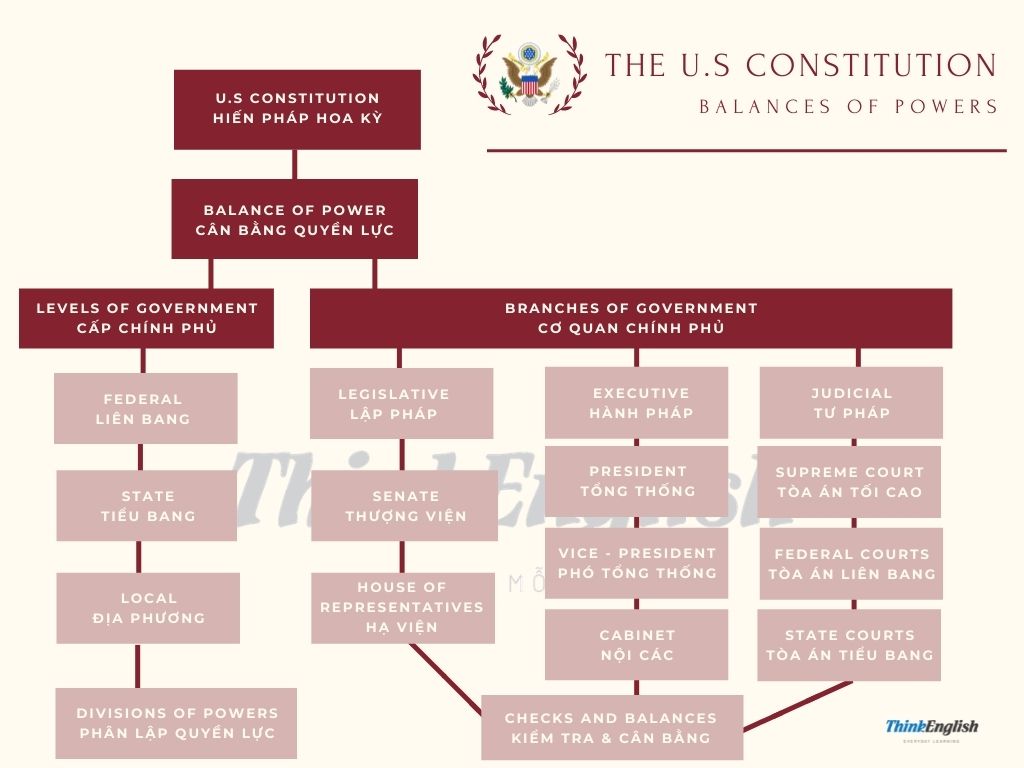
Cùng tìm hiểu từ vựng tiếng anh theo chủ đề United States Constitution: Balance of Power – Hiến Pháp Hoa Kỳ: Cán cân Quyền lực để cùng học với bé môn Social Studies nhé.
Xem thêm:
- Từ vựng chủ đề United States Constitution – Hiến Pháp Hoa Kỳ
- United States Constitution:Vocabulary Quiz – Trắc nghiệm Từ vựng về Hiến pháp Hoa Kỳ
- United States Constitution: Word Search – Game Tìm từ vựng đề tài Hiến pháp Hoa Kỳ
United States Constitution (Hiến pháp Hoa Kỳ) – Cán cân quyền lực
U.S Constitution: Hiến pháp Hoa Kỳ
The constitution written at the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787 and subsequently ratified by the original thirteen states
→ The U.S Constitution is the supreme law of the United States of America.
—
Balance of Power: Cân bằng quyền lực
Distribution of power in which no single nation is able to dominate or interfere with others
→ The balance of power must be maintained.
—
Level of Government: Cấp chính phủ
Government in the United States consists of three separate levels: the federal government, the state governments, and local governments.
→ Historically, all the constitutional negotiations have taken place between those levels of government.
—
Federal Government: Chính quyền Liên bang
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic in North America, composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories and several island possessions.
→ The US federal government has been mandated to embrace the Energy Star Program.
—
State Government: Chính quyền các tiểu bang
State governments of the United States are institutional units in the United States exercising functions of government at a level below that of the federal government.
→ Companies in the US are obliged to give assets that they believe are abandoned to US state governments.
—
Local Government: Chính quyền địa phương
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state.
→ Local governments generally act only within powers specifically delegated to them by law and/or directives of a higher level of government.
—
Divisions of Powers: Phân lập quyền lực
The principle that sovereignty should be divided between the federal government and the states especially as expressed by the Constitution of the U.S.
→ Before 1993, Andorra’s political system had no clear division of powers into executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
—
Branches of Government: Cơ quan chính phủ
To ensure a separation of powers, the U.S Federal Government is made up of three branches: legislative, executive and judicial.
→ The Constitution created a unitary state governed by three branches of government: the executive, legislative and judicial branches.
—
Legislative: Lập pháp
Makes laws (Congress, comprised of the House of Representatives and Senate). The legislative branch drafts proposed laws, confirms or rejects presidential nominations for heads of federal agencies, federal judges, and the Supreme Court, and has the authority to declare war.
→ The president can veto legislation created by Congress and nominates heads of federal agencies.
—
Senate: Thượng viện Hoa Kỳ
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
→ On 6 January 1999, then US President Bill Clinton recommended that the US Senate ratify both agreements.
—
House of Representatives: Hạ viện Hoa Kỳ
The United States House of Representatives is the lower house of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper house. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
→ There will be at least 20 new members of the House of Representatives.
—
Executive: Hành pháp
Carries out laws (president, vice president, Cabinet, most federal agencies). The executive branch carries out and enforces laws. It includes the president, vice president, the Cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees.
→ Much of the work in the executive branch is done by federal agencies, departments, committees, and other groups.
—
President: Tổng thống
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America.
→ This was the initiative US President Donald Trump mentioned during his telephone conversations with Russian President Vladimir Putin.

Vice-President: Phó Tổng thống
The vice president of the United States is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession.
→ In 2006, Blanchett joined former US Vice–President Al Gore’s Climate Project.
—
Cabinet: Nội các
Cabinet members serve as advisors to the president. They include the vice president, heads of executive departments, and other high-ranking government officials.
→ Cabinet members are nominated by the president and must be approved by a simple majority of the Senate—51 votes if all 100 Senators vote.
—
Judicial: Tư pháp
The judicial branch interprets the meaning of laws, applies laws to individual cases, and decides if laws violate the Constitution. It is comprised of the Supreme Court and other federal courts.
→ Article III of the Constitution, which establishes the Judicial Branch, leaves Congress significant discretion to determine the shape and structure of the federal judiciary.
—
Supreme court: Tòa án tối cao
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. The Justices of the Supreme Court are nominated by the president and must be approved by the Senate.
→ The Court meets in the Supreme Court Building in Washington, D.C.
—
Federal court: Tòa án Liên bang
The Constitution gives Congress the authority to establish other federal courts to handle cases that involve federal laws including tax and bankruptcy, lawsuits involving U.S. and state governments or the Constitution, and more. Other federal judicial agencies and programs support the courts and research judicial policy.
→ “US federal courts have a long history of swiftly and fairly trying terrorism suspects,” said Prasow.
—
State court: Tòa án tiểu bang
In the United States, a state court has jurisdiction over disputes with some connection to a U.S state.
→ The California Supreme Court and all lower California state courts use a different writing style and citation system from the federal courts and many other state courts.
—
Checks and Balances: Kiểm soát và cân bằng
Checks and balances are various procedures set in place to reduce mistakes, prevent improper behavior, or decrease the risk of centralization of power
→ Checks and balances usually ensure that no one person or department has absolute control over decisions, clearly define the assigned duties, and force cooperation in completing tasks.
—
Sơ đồ Cán cân quyền lực của Hiến pháp Hoa Kỳ